Causes and risk factors to Hair Loss
What is the cause of excessive hair loss?
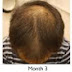
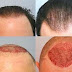
A number of factors can cause excessive hair loss. For example, about 3 or 4 months after having a disease or have undergone major surgery, you may suddenly lose in a lot of hair. This type of hair loss is related to the stress of illness and is temporary.
Hormonal problems may cause hair loss. If the thyroid gland is overactive or underactive, your hair may fall out. Usually this type of hair loss can be controlled by the treatment of thyroid disease. Hair loss may occur if there is an imbalance in the male or female hormones, known as androgens and estrogens. Correcting the hormone imbalance may stop the hair loss.
Many women notice that their hair about 3 months after having a baby . This drop is also related to hormones. During pregnancy, high levels of certain hormones cause the body to keep hair that normally would fall. When the hormones return to pre-pregnancy levels, that hair falls out and starts the normal cycle of growth and decline again.
Some medicines can cause hair loss. This type of hair loss improves when you stop taking the medicine. Medicines that can cause hair loss include blood thinners (also called anticoagulants), medicines used to treat gout, high blood pressure or heart problems; vitamin A (if too much is taken); birth control pills and antidepressants.
Determined infections can cause hair loss. Fungal infections from the scalp can cause hair loss in children. For the infection is easily treated with antifungal medications.
Finally, hair loss may occur as part of an underlying disease, such as lupus or diabetes. Since hair loss may be an early sign of a disease, it is important to determine the cause able to treat it.
A number of factors can cause excessive hair loss. For example, about 3 or 4 months after having a disease or have undergone major surgery, you may suddenly lose in a lot of hair. This type of hair loss is related to the stress of illness and is temporary.
Hormonal problems may cause hair loss. If the thyroid gland is overactive or underactive, your hair may fall out. Usually this type of hair loss can be controlled by the treatment of thyroid disease. Hair loss may occur if there is an imbalance in the male or female hormones, known as androgens and estrogens. Correcting the hormone imbalance may stop the hair loss.
Many women notice that their hair about 3 months after having a baby . This drop is also related to hormones. During pregnancy, high levels of certain hormones cause the body to keep hair that normally would fall. When the hormones return to pre-pregnancy levels, that hair falls out and starts the normal cycle of growth and decline again.
Some medicines can cause hair loss. This type of hair loss improves when you stop taking the medicine. Medicines that can cause hair loss include blood thinners (also called anticoagulants), medicines used to treat gout, high blood pressure or heart problems; vitamin A (if too much is taken); birth control pills and antidepressants.
Determined infections can cause hair loss. Fungal infections from the scalp can cause hair loss in children. For the infection is easily treated with antifungal medications.
Finally, hair loss may occur as part of an underlying disease, such as lupus or diabetes. Since hair loss may be an early sign of a disease, it is important to determine the cause able to treat it.








Post a Comment